Halide abstraction
One way to reactive cations - stabilized by the weakly coordinating anions [Al(ORF)4]- - is the abstraction of a halide anion with the silver salt Ag[Al(ORF)4] from a halogene containing compound like CX4 or PX3. The driving force in these reactions is the big lattice energy of the precipitating AgX. In case of the tetrahalomethanes CX4 (X = Cl, Br, I) this leads directly to the trihalocarbenium cations [CX3]+. With the phosphorus trihalides PX3 (X = Br, I) an electrophilic carbene-analogous [PX2]+ intermediate (not isolable) is built, which can insert in different bonds like X-X, X2P-X (X = Br, I) or in a P-P bond of white phosphorus (P4) for example.
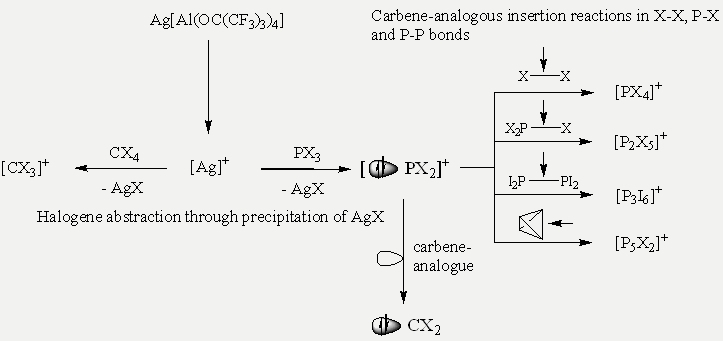
On this way the halocarbenium cations [CX3]+ (X = Cl, Br, I) and several reactive phosphorus cations were isolated as salts of the [Al(ORF)4]- anion and could be characterized in solution and in the solid state by X-Ray diffraction, vibrational (Raman and IR) and NMR spectroscopy (especially 13C and 31P).
Literature:
[CCl3]+ und [CBr3]+:
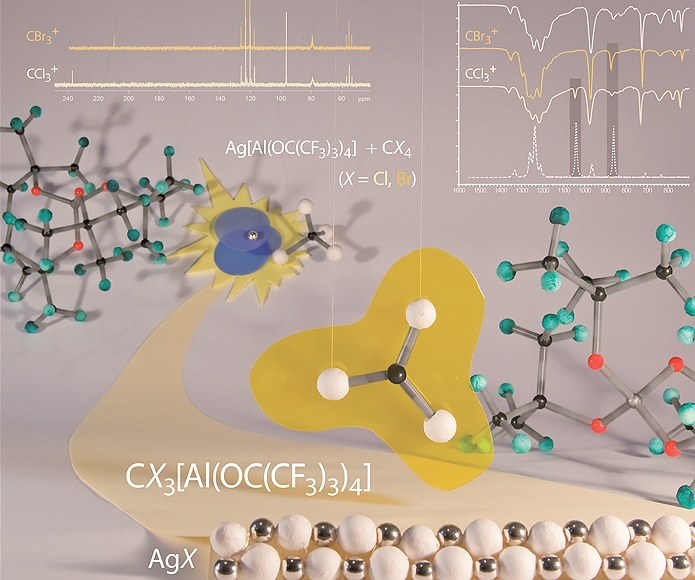
A. J. Lehner, N. Trapp, H. Scherer, I. Krossing, Dalton Transactions 2010, 40, 1448.
[CI3]+
I. Krossing, A. Bihlmeier, I. Raabe, N. Trapp, Angewandte Chemie 2003, 115, 1569.
I. Raabe, D. Himmel, S. Muller, N. Trapp, M. Kaupp, I. Krossing, Dalton Transactions 2008, 946.
[P5X2]+ (X = Br, I)
I. Krossing, I. Raabe, Angewandte Chemie 2001, 113, 4544.
[PX4]+, [P2X5]+ und [P5X2]+ (X = Br, I)
![halide-abstraction-[P2I5]-synt.gif halide-abstraction-[P2I5]-synt.gif](https://www.molchem.uni-freiburg.de/research/reacat/halide-abstraction-P2I5-synt.gif)
[P2I5]+ from P2I5[Al(OC(CF3)3)4]
M. Gonsior, I. Krossing, L. Müller, I. Raabe, M. Jansen, L. van Wüllen, Chemistry – A European Journal 2002, 8, 4475.
[P3I6]+ and [P5I2]+
![halide-abstraction-[P2I5]-calc.gif halide-abstraction-[P2I5]-calc.gif](https://www.molchem.uni-freiburg.de/research/reacat/halide-abstraction-P2I5-calc.gif)
[P5I2]+ calculated (RI-MP2/TZVPP)
I. Krossing, Journal of the Chemical Society, Dalton Transactions 2002, 500.

